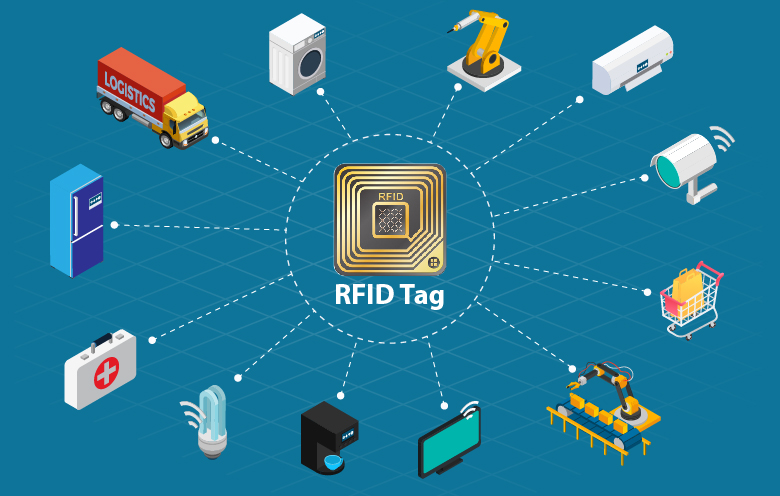
Do you know that one of the oldest wireless technologies is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)? Patented by the late British inventor Charles Walton in 1983, RFID made it possible for new, state-of-the-art technology, near-field communication (NFC), to exist.
Think of an Internet-free IoT existence. For the most part, we can’t, right? NFC makes it possible. Not only does NFC allow connecting the unconnected, but it also permits bidirectional communication, consumes less power compared to Bluetooth, connects electronic devices with a single tap and provides multi-level data security. Like NFC, RFID takes an IoT setup to wide-ranging adoption. Let’s dissect IoT a little to understand that. IoT requires a few components to enable devices and objects to communicate. First, it is necessary to identify objects uniquely. Second, the object should be able to transmit data wirelessly. Here comes an RFID tag’s role.

How to achieve increased worker safety and productivity with IoT
Webinar agenda
- Impact of digital transformation and the opportunities it brings
- Major risk factors for workers
- Real-world connected worker use cases to improve safety
- What steps you can take to get started
Smart objects will be embedded with both a sensor and an RFID tag. Depending on the type of sensor, it can capture surrounding temperature fluctuations, quantity changes, or other information types. And an RFID tag uniquely identifies the object. The information from the smart object travels to a central database via IP networks that stores and sorts the data into a human-readable format. In addition, sensors, RFID tags and IP networks are common in households, offices, warehouses, parks and many other places today. Thus, the combination of RFID and IoT is slowly establishing its solid presence in a variety of industries, ranging from manufacturing to logistics to healthcare and retail.
For decades, RFID technology has been in use. It offers clear advantages over printed bar codes. While bar codes generally identify an object, RFID can locate a particular individual object. Through links to a cloud-based reference database, RFID offers the ability to fully trace an item – including learning about its size, serial number, color, batch, when and where it was made, by whom, under what conditions, etc. Furthermore, unlike bar codes, for reading, RFID labels do not need to be visible. That’s why amongst all Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) technologies – a barcode, a data matrix and a QR code – RFID is leading the cadre.
The image below will help you understand the basics of RFID:
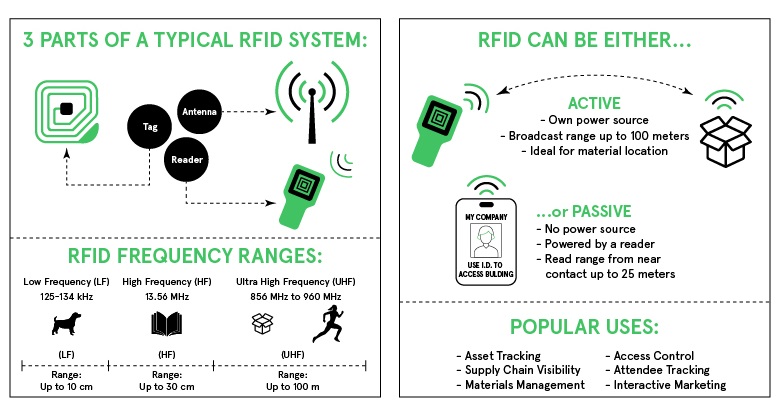
Let’s now dive into some of the real-world examples that show how RFID and IoT are flying together to reach new heights.
RFID and IoT in laundry service
One of the pleasures of staying in a hotel is having someone else take care of your daily tasks. But most of us don’t think about where all those fresh towels and bed linens come from (and go to) every day.
The cost of laundry is a significant expense for hotels, restaurants, hospitals, resorts, care facilities, and manufacturing and pharmaceutical companies. With IoT-based applications, their linens can now hone in on their costs with a level of accuracy never seen before.
For example, Berendsen UK (now Elis), a major UK-based laundry company, now has full visibility into the location of every item, at any time. Although the history of Berendsen can be traced back over 160 years, shipping a million items every day from 50 sites throughout the UK, the vast majority of its activities remained a manual process. The handling and tracing of each piece of clothing was, therefore, nothing more than a mere thought. In addition, thinking about keeping costs under control in the laundry wasn’t even a concept before IoT.
However, Berendsen has installed RFID tags in every piece of their textiles – from bed sheets, pillowcases, tablecloths, napkins to towels – to track the status. It also helps them to know exactly how much stock they hold and wherein the washing, delivery and collection cycle all of their RFID tagged laundry is. Not only that, with data from smart meters, Berendsen can monitor the costs of using hot and cold water, electricity and chemicals in washing.
On an aggregate level, they have a holistic view of the health of laundry operations, all of which translates into massive savings.
RFID and IoT for baggage tracing and handling
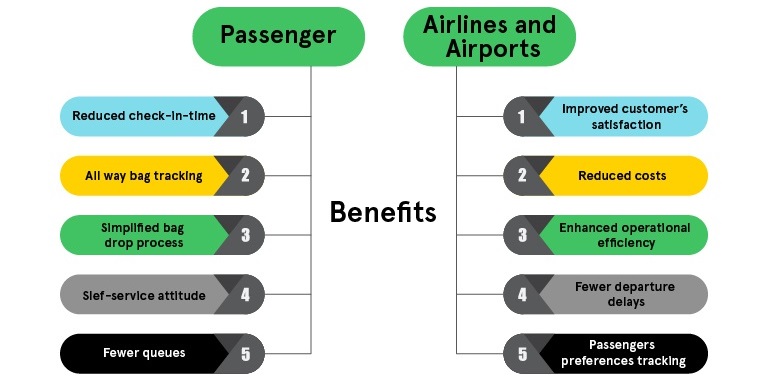
At some point or another, nearly every air traveler faces issues with their baggage while at the airport. These can be bag misplacement, lost items, excessive waiting time, etc. RFID baggage tracking technology can be used to get rid of such problems and make your airport experience smooth. Delta is the first US carrier to use RFID technology to track baggage.
For Delta, the traveler must have the airline’s mobile app, where push notifications help travelers know their baggage location while on their way to the aircraft, on the plane, and when the baggage is
on the way to the baggage claim counter. Delta has achieved an eye-popping 99.9% tracking success rate by embedding RFID chips in each luggage, making it one of the best among US global airlines.
Airlines and airports not only benefit from taking care of customer headaches and increasing their satisfaction rate, but the technology also brings benefits to them as mentioned below.
RFID and IoT for retail
After Amazon Go stores, Chinese retailer JD.com is taking its steps towards the unmanned store of the future using RFID. Besides, improving the checkout counter experience, in October 2016, Macy’s went public with its intention to tag 100% of its merchandise with RFID by the end of 2017. To date, RFID tagging has helped Macy’s to reduce the inventory variance from 4-5% per month to 2-4% and cut display shortages from 30 to 4-6%.
RFID tags are placed on the goods and they send data to an IoT platform where it is stored and analyzed. With that, inventory managers get alerts if a specific item runs low or its date is expiring shortly. Connected devices are therefore crucial to avoid over-supply, shortage of goods and store theft. By tracking inventory, they allow stress reduction, elimination of operating errors and cost savings.
In all, the large-scale commercialization of machine-to-machine communication has stimulated a fourth industrial revolution and RFID tags are vital to it. In an increasingly connected world, these tags are essential components to identify and track any item in real-time. As a result, supply chains can become more efficient and customization of the product can be brought to the next level. Contact us to realize how RFID can track your stock, streamline operations and improve your business.