The days of advanced data analytics being a ‘nice-to-have’ are over. Now, it’s the need of the hour. To accelerate business growth and make strategic decisions, business owners need to get into the ins and outs of the business process, industry competitors, customers, and market.
This is where Power BI shines. Power BI is a versatile platform that adapts to your needs. Whether you are new to analytics or have decided to enforce a business intelligence platform, Power BI is the choice.
Market share of business intelligence tools
The market analysis tells us that Power BI is one of the popular business intelligence tools.
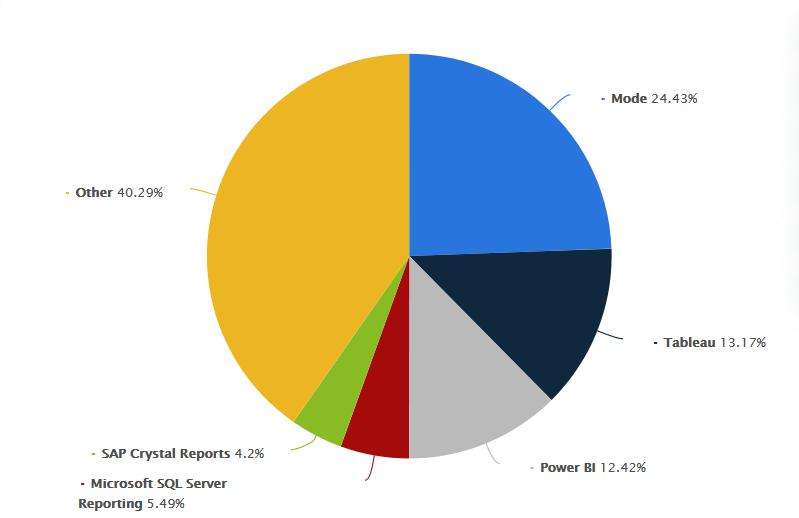
Source: Statista
On top of it, Power BI was ranked a leader in the 2022 Gartner Magic Quadrant for the whopping 15th consecutive year.
Benefits of Power BI migration
1. Flexible system integration
Power BI is built on the Azure cloud and is recognized not only for its scale and reliability but for flexibility as well. This means that you can integrate the platform with limited hustle by integrating it with Excel, Microsoft Teams, and other solutions. More specifically, while advanced BI reporting can be combined with Microsoft Azure cloud solutions, it can also be connected to and operated with other cloud data warehouses and on-premises and third-party databases.
2. Cutting-edge visualization
Booming with the use of low-code to no-code tools, the analytics that are kept in Power BI are rather easily consumable by the employees. While self-service analytics can be of significant benefit, with this in place, decision-makers can make decisions for change-of-the-game much quicker and more effective.
Furthermore, updates are released once a month for Power BI Desktop with both small and major changes that include:
- New data connectivity options
- Modeling elements
- Reporting capabilities
- Visualizations and tools
- Enhanced error detection or diagnostics
- Better support
- Improvements in infrastructure, in the performance of Power BI and much more.
Microsoft also incorporates the feedback from the users in enhancing the visualizations and they made provision for users to select reports into filters and dashboards based on metrics where users can even adjust in real-time and receive Newest Filter Requirement updates.
3. Cost-effectiveness
Power BI is available for download and can work as a free demo for a limited amount of time. The monthly plans are $10 – $20, with the ‘bigger data & AI’ add-on offering access to additional big data and AI tools.
However, the price is rather low compared to the quality of the service that the clients could receive. Consequently, they get you the low cost versus quality, which in turn provides total cost of ownership (TCO) benefits.
4. Real-time data access
Once the data has been transferred into our system, the data is processed and loaded into interactive reports and graphs so that it may be processed in real-time. It provides you with such a significant competitive advantage in terms of the speed of data processing and updates, and not only in terms of uncovering the value-added value territory of insights but in terms of rapidly solving matters, modeling prospects, and dealing with timed-out data.
Interesting Read: 5 industries that are revolutionized by Power BI
Power BI migration steps
Here’s the plan on how to conduct the migration.
Migrating BI assets to Power BI
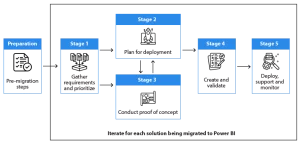
Before proceeding to the five key stages of migration, it’s vital to implement pre-migration steps:
- The cost benefit analysis and evaluation respective
- Defined stakeholders and support from top management
- Initial governance model generation
- Initial deployment planning
- Initial architecture establishment
Stage 1: Requirements gathering
This stage is self-explanatory. It’s a recurring step where during the process, you gather requirements and rank them for future transitioning. Thus, there is an opportunity to evaluate the state of the existing BI items and identify which of them require change or refactoring in the next Power BI environment.
For reports requirements gathering there are likely be needed information such as purpose, audience, and expected action. It is also important to identify the elements that users engage with while using the reports to determine which ones can be completely removed or enhanced in the new architecture. It is worth defining who will be responsible for certain reports as owners and/or subject matter experts (SMEs) in charge of change management, approval, and signoff.
Other essential activities are also included in this stage, such as security requirements analysis. Here is where you should explain aspects of role-based access control, data sensitivity and privacy issues, regulatory requirements, and compliance considerations. However, also be prepared to name the potential threats and issues, better yet known drawbacks.
Reports requirements identification necessitates, first and foremost, data requirements compilation and prioritization as a similarly rigorous and timely concept. The key aspects for work here include:
- Existing reports queries
- Data source types
- Data structure and cleansing
- Data integration
- The amount of data involved, the need for scale, and the tolerance for latency
- Security and privacy.
Stage 2: Deployment plan
The features’ requirements can then be put into an iterative, non-linear deployment plan, once all requirements are analyzed and sorted according to priority.
The first decision tends to be where to go: Power BI-service or Power BI-reporting server. Microsoft notes that one of these products should be used since they are more stable in comparison to the security, content dissemination, etc., than Power BI Desktop.
Then, it’s important to decide on the workspace management approach: if you would prefer to have a new workspace at all, or if you would be able to manage with a single workspace for data and reports or if you’d require several workspaces and finally, what would be the security settings of the workspaces.
Next: How will it be implemented, and the product be used? Does it concern only access through a Power BI app, enterprise tools (Teams, SharePoint Online, a corporate portal), or mobile devices? Well, that is left to your discretion.
Stage 3: Creation of proof of concept
There is no question that one of the most crucial processes in this stage is to outline and document PoC goals and objectives here; these are to understand more about initial requirements and how data works to discover potential problems. To ensure that the necessary data source can connect and to check all the functionalities and security settings; to tinker with the layout and other design-related choices.
In the PoC creation stage, some basic differences may also arise in Power BI, and there might be a need for changes in the data architecture of the business, and the proposal for handling the conversion of the Business intelligence dashboards also comes under this stage.
Stage 4: Creating the content and checking the facts
The PoC realized during this stage consists in translating the proof of concept into a producible solution capable of delivering the benefits envisaged for the organization while applying the knowledge acquired during the PoC development stage. And — if time allows — approaching individuals responsible for this very occurrence.
If an existing Power BI dataset doesn’t meet your needs, you can enhance it or develop a new one by:
- Collecting data across one or even multiple data sources
- Transformation, melding and formation of data
- Training an ideal set of datasets
- Checking model relationships
- Implementing row-level security.
The next step for abstraction is to create new reports and new dashboards and to select data visualization tools, specifying exactly those terms that are to be used and as much avoiding acronyms and specialized language as possible, how to deal with interactivity.
Stage 5: Deployment and support
The last step in the migration process involves the final preparations that would make the solution ready for use.
To achieve this, first, the solution needs to be installed in the test environment and initiate user acceptance testing. After doing so, the team should then implement it for the production environment and then conduct the retrospective.
Minimizing risk: In order not to lose important future mission reports, the new solution should be tested for a certain period parallel to the old one.
After the migration has been performed and completed with success, then one must start controlling the solution. For instance, they include control activity logs, content update, subscriptions to new feeds, and any other pertinent variables. At some point, it would be useful to know whether the migration solution may need further modification as the enterprise expands. That is why post-migration support is a must, whether it is inner or outer migration support services.
Conclusion
Migrating to Power BI can be a cumbersome process with unique considerations for each business. To ensure a smooth transition, consider shaking hands with an organization that is an expert in Microsoft Power BI consultancy. If you’re looking to migrate Power BI from one tenant to another, we can assist you. At Softweb Solutions, we’ll analyze your specific needs, develop a tailored migration strategy that minimizes risk and optimizes your total cost of ownership, and handle the entire implementation process – all while providing ongoing support after the migration is complete.









